Low LOD 1-Step RT-qPCR Master Mix
Low LOD 1-Step RT-qPCR Mix is fast, highly reproducible real-time PCR master mix that has been designed with a highly optimized buffer chemistry and hot-start DNA polymerase, to deliver excellent results and very low background, allowing greater sensitivity.
Have questions about a product?
Contact us to learn more about Meridian’s molecular or immunoassay reagent portfolio. We want to hear from you!
Low limit of detection (LOD) for both RNA and DNA viruses
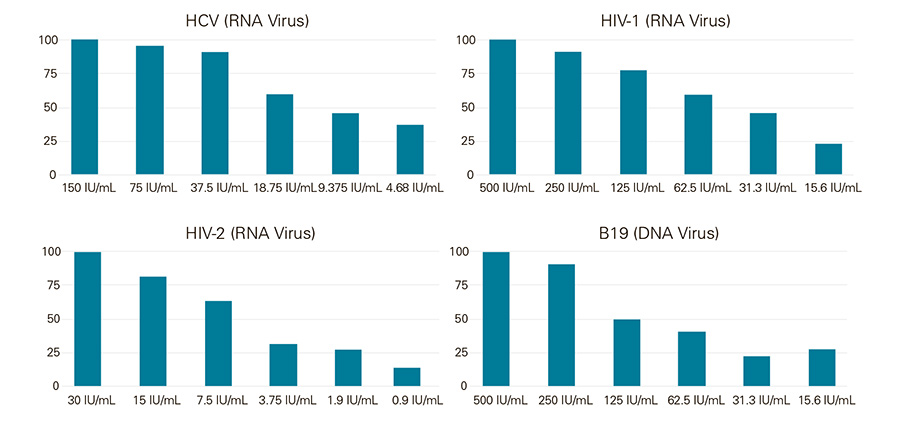
24 replicates of purified blood viral extracts were tested in singleplex qPCR reactions using the Low LOD 1-Step RT-qPCR Mix at the indicated IU/mL. The singleplex reactions were HCV, HIV-1, HIV-2 and Parvovirus B19. The amplification curve results illustrate that Low LOD 1-Step RT-qPCR Mix can be used with both RNA and DNA viruses as low as 5 IU/mL
Low LOD 1-Step RT-qPCR Mix, MDX025
RT-qPCR mix a dNTP/dUTP mix, designed for stringent amplification of highly structured and very low copy-number RNA and DNA targets.
Documents & Resources
Description
Low LOD 1-Step RT-qPCR master mix contains Taq DNA polymerase, reaction buffer, dNTP, MgCl2, stabilizers, and PCR enhancers, and a separate RNase tolerant reverse transcriptase mix. However, the dTTP in the dNTPs has been substituted for dUTP, so that Uracil DNA Glycosylase (UDGase) (MDX054) can be added to remove background PCR product contamination. This makes Low LOD 1-Step RT-qPCR ideal for developing highly sensitive RT-qPCR diagnostic tests, such as for detecting RNA and DNA viruses at very low levels in blood banks or transplant viral testing.
Specifications
| Description | RT-qPCR mix containing Taq polymerase, reaction buffer, MgCl2 and optimized dNTP/dUTP mix, and separate reverse transcriptase/RNase inhibitor mix, designed for stringent amplification of highly structured and very low copy-number RNA and DNA targets. |
| Concentration | 2x |
| Appearance | Clear, colorless solution |
| Hot Start | Antibody mediated |
| dUTP | Presence of dUTP checked by reverse-phase HPLC separation |
| Application | Probe-based, one-step RT-qPCR |
| Sample type | RNA and DNA |
| Presentation | 2 vials |
| Storage | -20 °C |
| Mix stability | See outer label |
| Consistency | ±0.5 Ct variance between test and reference sample |
| DNase/RNase Contamination | No detectable degradation |
Catalogs & Brochures
Low LOD 1-Step RT-qPCR MixLow LOD 1-Step RT-qPCR Mix
Lyo-Ready 1-Step RT-qPCR MixesLyo-Ready 1-Step RT-qPCR Mixes
Master Mixes for Molecular Ambient-Temperature Stable AssaysMaster Mixes for Molecular Ambient-Temperature Stable Assays
FAQs: Low LOD 1-Step RT-qPCR Mix
In one-step RT-qPCR or reverse transcription qPCR, cDNA synthesis and qPCR are performed in a single reaction tube. In two-step qPCR, cDNA is synthesized in one reaction tube, and aliquots of the cDNA is then used for a subsequent qPCR experiment.
• Accurate representation of target copy number
• Simple and rapid
• Fewer pipetting steps (reducing possible errors and contamination)
• Best option for high-throughput screening
• Best method when only a few assays are run repeatedly
• Multiplex qPCR of gene of interest and control can be done in single well, from same RNA sample
There are several other advantages of one-step reactions, these include limited sample handling and reduced bench time, which helps to decrease chances for pipetting errors and cross contamination between reverse transcription and qPCR steps. This method is quick to set up and makes processing multiple RNA samples easy (especially when using liquid handling robotics), when you are amplifying only a few genes of interest. It is therefore ideal for high throughput screening laboratories where only a few reverse transcription qPCR assays are run repeatedly, using well-established reaction conditions, with the added advantage that multiplex qPCR of the gene of interest and control genes can be done in single well, from same RNA sample.
Gene-specific primers are required for generating the cDNA and for subsequent amplification in one tube, however this reduces experimental variation, since both enzymatic reactions take place under the same conditions, making one-step qPCR highly reproducible.
One-step RT-PCR requires careful evaluation to prevent primer dimer formation, because the primers will be present during the lower temperature conditions of the RT reaction as well as the qPCR cycling. This is particularly important in multiplex qPCR assays.
As qPCR can amplify tiny amounts of DNA, preventing contamination is essential, as even small amounts of qPCR contamination can produce false positives. qPCR contamination can include cross-contamination from other samples, contamination from elsewhere in the laboratory, and carryover contamination from amplification products and primers used in prior qPCR experiments. The latter causes most of the false positive results seen in qPCR. Preventing contamination can be difficult and so laboratory procedures must be in place to ensure DNA from one assay is not re-amplified in subsequent assay.
Uracil DNA Glycosylase can specifically degrade products that have already been through the qPCR process and have incorporated dUTP, leaving native nucleic acid templates intended for amplification intact. Uracil DNA Glycosylase activation occurs as the first step of qPCR at a 50°C incubation for 2 minutes and then the Uracil DNA Glycosylase is denatured when the temperature increases to 95°C during hot-start activation.
Uracil-DNA glycosylase (UDG or UDGase) is a family of enzymes comprising six sub-families. Family I UDGase enzymes are called UNG (uracil-N-glycosylase gene), so there is no difference, the terms UDG and UNG are commonly used interchangeably because they perform the same function in qPCR—namely to prevent carryover qPCR contamination.
Get in Touch With A Specialist
Have questions about a product? Want to learn more about Meridian’s molecular or immunoassay reagent portfolio? We want to hear from you!